会议时间:3月21-22日
会议地点:福建·仙游 中国古典工艺博览城
报告人:Francis Gichuhi MBURU
Senior lecturer, Head of Forestry and Wood Science Department, University of Eldoret, Kenya
Abstract
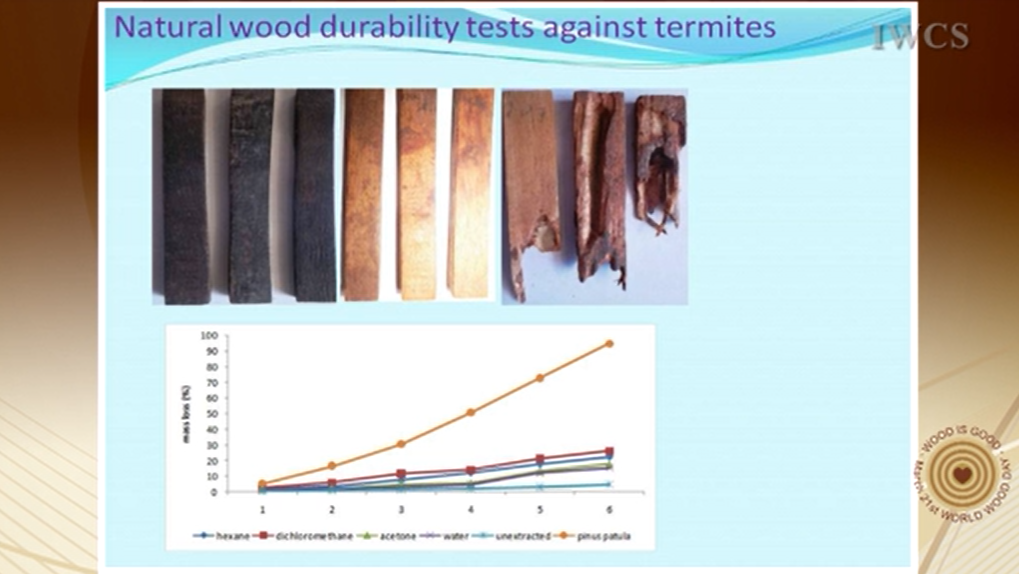
Studies were carried out on termite and fungal resistance of the lesser known Albizia malacophylla Kenyan wood species. In addition wood dimensional stability, amount and chemical nature of heartwood extractives was also evaluated. Wood resistance against white rot tropical fungi was based on a laboratory soil bed test and subterranean termite resistance in the field according to American Wood Protection Association: E7-93 (1993) standard. Wood extractives were subjected to infra-red analysis using standard laboratory procedures. Albizia malacophylla heartwood is dimensionally stable (5.5 %) with a less dimensionally stable sapwood (9.6 %). Heartwood extractive content is high (9.7 %) in comparison to sapwood (4.6 %). Albizia malacophylla heartwood is resistant to fungi (8.1 %) mass loss and very resistant to termites (4.8 %) mass loss reported after 6 months exposure. Removal of extractives significantly lowered heartwood dimensional stability, termite and fungus resistance. Heartwood extractives were able to inhibit the growth of fungi under laboratory sterile conditions. Infra-red analysis of crude heartwood extractives indicated presence of aldehydes, ketones carbonyl compounds, esters, aromatic,carboxylic acids and aliphatic carbonyl compounds. Put together, the nature, amount of heartwood extractives and wood dimensional stability are at the origin of the found termite and fungus resistance of A. malacophylla wood.
Speaker Biography
Dr. Francis Gichuhi MBURU, Senior lecturer, Head of Forestry and Wood Science Department, University of Eldoret, Kenya
My interests are in Wood processing, Wood preservation, Wood degradation science, Pulp and Paper Science, Microscopy, Minor wood and Forest products.
责任编辑:iwcs25Z/H

 3,076
3,076