会议名称:“2022世界木材日”研讨会暨第四届国际林联(IUFRO)林产品文化研究组讨论会
会议时间:2022年3月21日
报告嘉宾:Olusola Samuel Areo
嘉宾简介:尼日利亚林业研究所(FRIN)首席研究员
摘要:
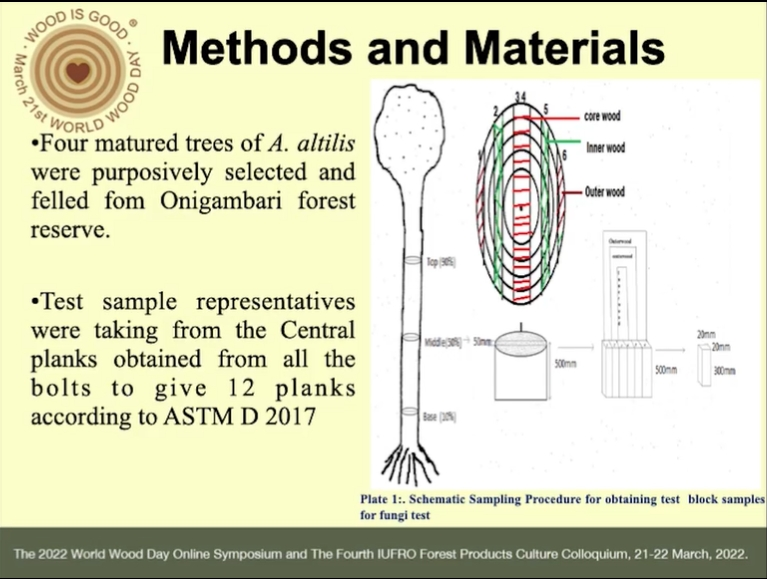
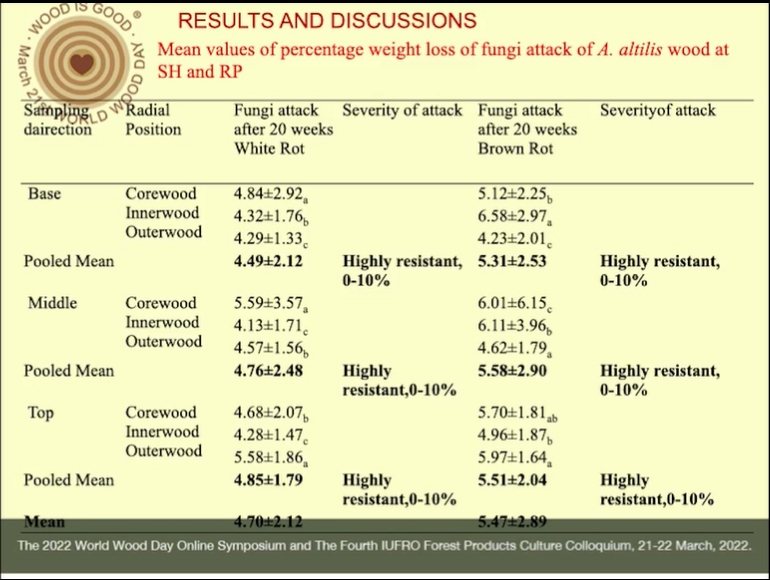
Nigeria wood based industries are facing a severe shortage and scarcity of choice timber species and to meet this demand led to the introduction of (LUS) artocarpus altilis into timber market as an alternative wood species necessitated the need to evaluate its durability of wood in service in order to curtail deterioration by bio-deteriorating agents. Four A. altilis trees from Southwest zones of Nigeria were purposively selected and felled based on maturity (45±0.5 years). Billets (500cm) were obtained from (10% base, 50% middle and 90% top) of merchantable height of each tree and partitioned into centrewood, innerwood and outerwood along the radial 45 plane. Wood samples were inoculated with Xylaria polymorpha and Sclerotium rolfsii for 20 weeks in an accelerated durability test (ADT) using ASTM D-2017 standard. Analysis of variance at α0.05 was used for analysis. The result shows that A. altilis wood species is resistant to fungus attack, with an average weight loss of white and brown rot fungi 4.70±2.12g and 5.47±2.89g, respectively. Axially, white rot degraded wood by 4.49±2.12%, 4.76±2.48% and 4.85±1.79% and brown rot degraded wood by 5.31±2.53%, 5.58±2.90% and 5.51±2.04% at the base, middle and top respectively. The highest WL of 6.58±2.97% was obtained for innerwood. Analysis of variance showed that there was no significant difference in the weight loss of wood obtained from the 3 different sampling height positions and across the plane axis for the species. The effect of interaction between sampling height, radial position and fungi shows insignificant difference existed. However, according to the ASTM D-2017 (2008) classification for categorizing the resistance of wood species to decay fungi; however, wood samples of A.altilis species could be rated resistant (R).
责任编辑:iwcs25H

 946
946